Smarter City: How AI is enabling Mumbai battle COVID-19
When the COVID-19 pandemic hit Mumbai, one of the most densely populated cities in the world, the Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai (MCGM) promptly embraced newer technologies, while creatively utilising available resources. Here is a deeper dive into how the versatility of chest x-rays and Artificial Intelligence helped the financial capital of India in efforts to containing this pandemic.
The COVID-19 pandemic is one of the most demanding adversities that the present generation has had to witness and endure. The highly virulent novel Coronavirus has posed a challenge like no other to the most sophisticated healthcare systems world over. Given the brisk transmission, it was only a matter of time that the virus spread to Mumbai, the busiest city of India, with a population more than 1.5 times that of New York.
The resilient Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai (MCGM), swiftly sprang into action, devising multiple strategies to test, isolate, and treat in an attempt to contain the pandemic and avoid significant damage. Given the availability and effectiveness of chest x-rays, they were identified to be an excellent tool to rule-in cases that needed further testing to ensure that no suspected case was missed out. Though Mumbai saw a steep rise in cases more than any other city in India, MCGM’s efforts across various touchpoints in the city were augmented using Qure’s AI-based X-ray interpretation tool - qXR - and the extension of its capabilities and benefits.
In the latter half of June, MCGM launched the MISSION ZERO initiative, a public-private partnership supported by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Bharatiya Jain Sanghatana (BJS) and Desh Apnayen and CREDAI-MCHI. Mobile vans with qXR installed digital X-ray systems were stationed outside various quarantine centers in the city. Individuals identified to be at high-risk of COVID-19 infection by on-site physicians from various camps were directed to these vans for further examination. Based on the clinical and radiological indications of the individuals thus screened, they were requested to proceed for isolation, RT-PCR testing, or continue isolation in the quarantine facility. Our objective was to reduce the load on the centers by continuously monitoring patients and discharging those who had recovered, making room for new patients to be admitted, and ensuring optimal utilization of resources.
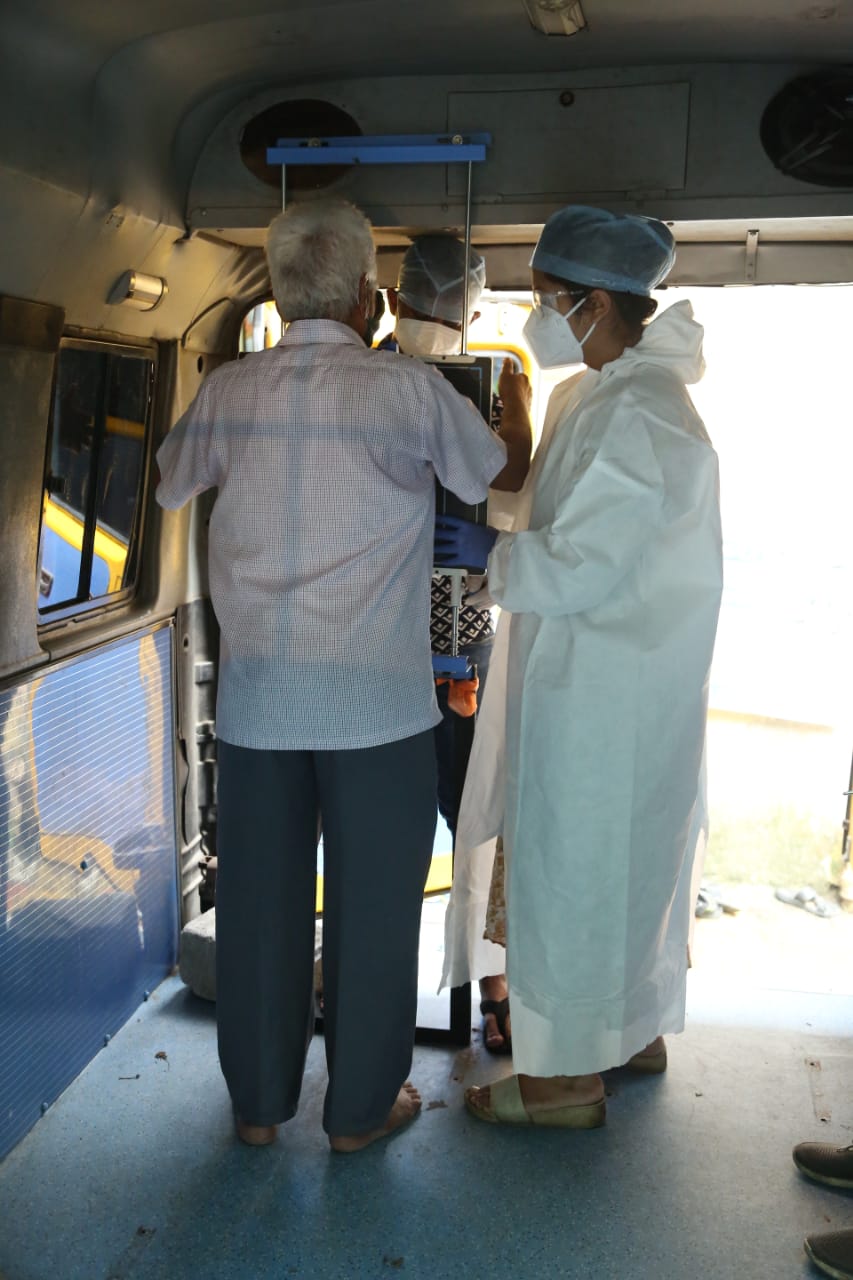

A patient being screen in a BJS van equipped with qXR
The approach adopted by MCGM was multi-pronged to ascertain that no step of the pandemic management process was overlooked:
- Triaging of high-risk and vulnerable and increase in case-detection in a mass screening setting to contain community transmission (11.4% individuals screened)
- Patient management in critical care units to manage mortality rates
- Support the existing healthcare framework by launching MISSION ZERO initiative and using chest X-ray based screening for optimum utilization of beds at quarantine centers
Learn more about Qure.ai qXR COVID in our detailed blog here
Triaging and Improvement in Case Finding
Kasturba Hospital and HBT Trauma Center were among the first few COVID-19 testing centers in Mumbai. However, due to the overwhelming caseload, it was essential that they triage individuals flowing into fever clinics for optimal utilization of testing kits. The two centers used conventional analog film-based X-ray machines, one for standard OPD setting and another portable system for COVID isolation wards
From early March, both these hospitals adopted
- qXR software - our AI-powered chest X-ray interpretation tool provided the COVID-19 risk score based on the condition of the patient’s lungs
- qTrack - our newly launched disease management platform
The qTrack mobile app is a simple, easy to use tool that interfaces qXR results with the user. The qTrack app digitizes film-based X-rays and provides real-time interpretation using deep learning models. The x-ray technician simply clicks a picture of the x-ray against a view box via the app to receive the AI reading corresponding to the x-ray uploaded. The app is a complete workflow management tool, with the provision to register patients and capture all relevant information along with the x-ray. The attending physicians and the hospital Deans were provided separate access to the Qure portal so that they could instantly access AI analyses of the x-rays from their respective sites, from the convenience of their desktops/mobile phones.
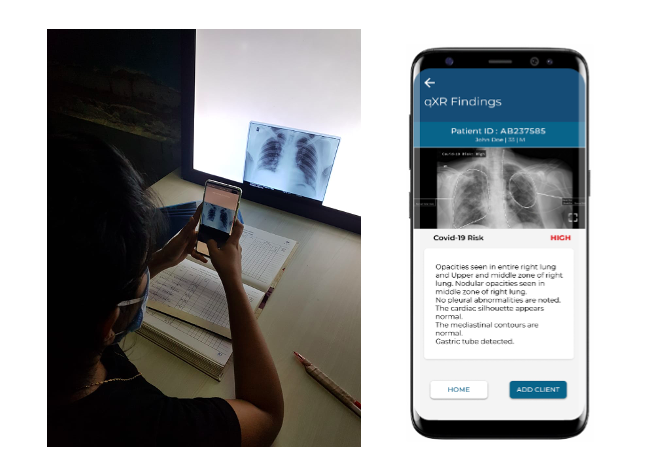
qXR app in action at Kasturba Hospital
Triaging in Hotspots and Containment Zones
When the city went into lockdown along with the rest of the world as a measure to contain the spread of infection, social distancing guidelines were imposed across the globe. However, this is not a luxury that the second-most densely populated city in the world could always afford. It is not uncommon to have several families living in close quarters within various communities, easily making them high-risk areas and soon, containment zones. With more than 50% of the COVID-19 positive cases being asymptomatic cases, it was imperative to test aggressively. Especially in the densely populated areas to identify individuals who are at high-risk of infection so that they could be institutionally quarantined in order to prevent and contain community transmission.
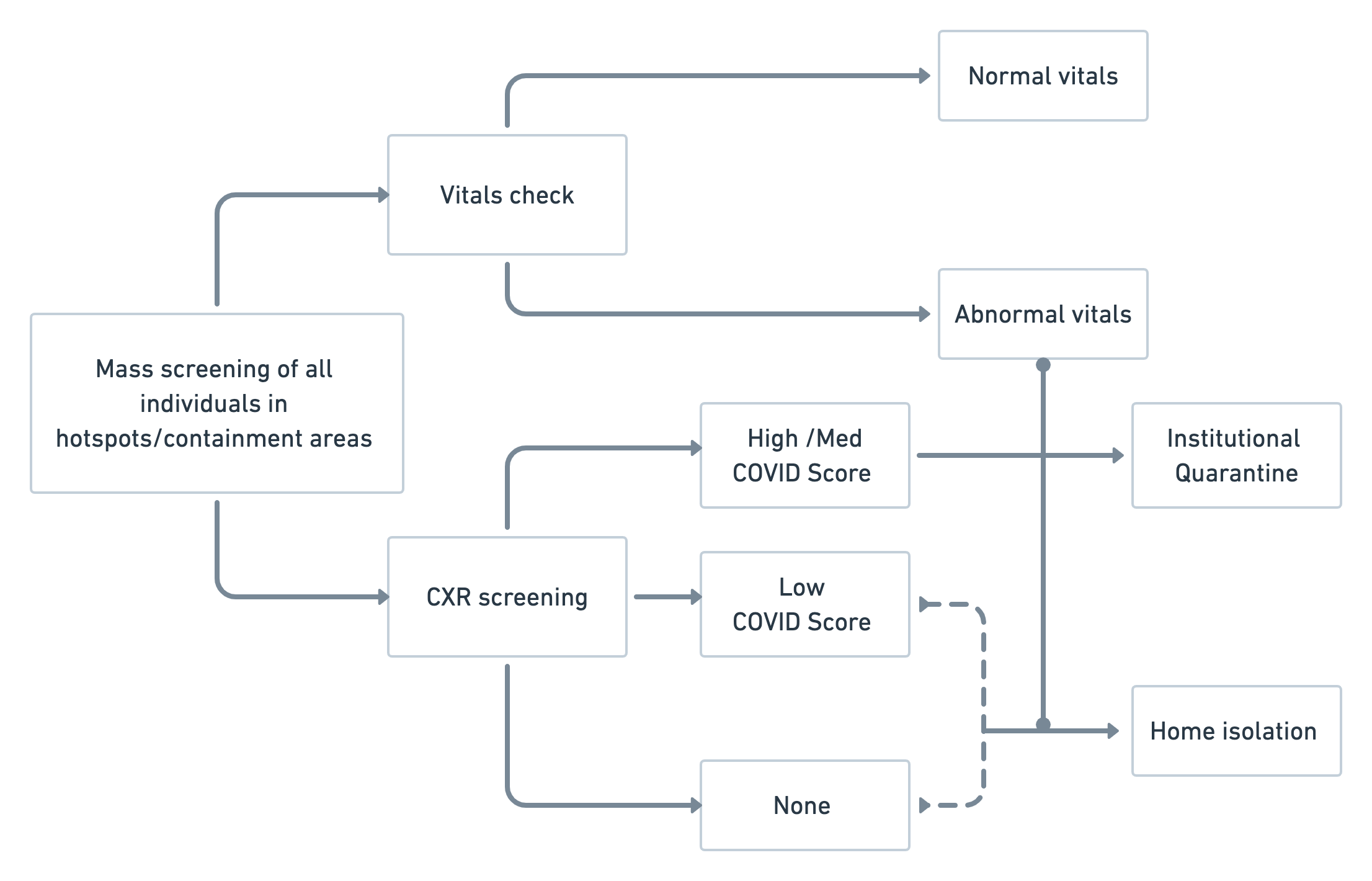
Workflow for COVID-19 management in containment zones using qXR
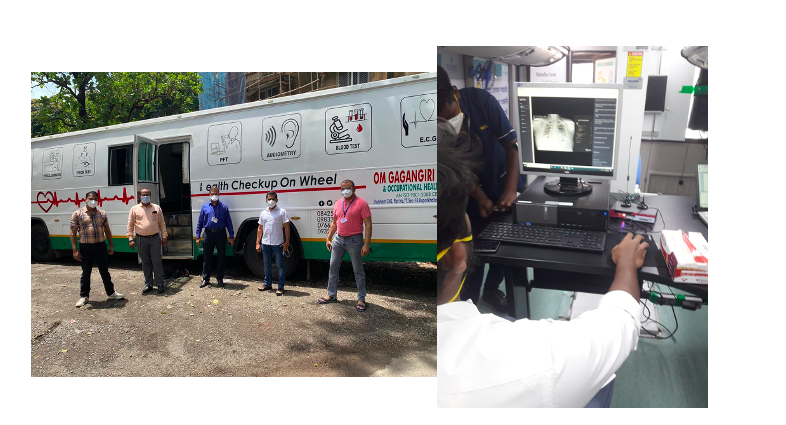

The BMC van involved in mass screenings and qXR in action in the van
Patient Management in Critical Care Units
As the global situation worsened, the commercial capital of the country saw a steady rise in the number of positive cases. MCGM, very creatively and promptly, revived the previously closed down hospitals and converted large open grounds in the city into dedicated COVID-19 centers in record time with their own critical patient units. The BKC MMRDA grounds, NESCO grounds, NSCI (National Sports Council of India) Dome, and SevenHills Hospital are a few such centers.
NESCO COVID Center
The COVID-19 center at NESCO is a 3000-bed facility with 100+ ICU beds, catering primarily to patients from Mumbai’s slums. With several critical patients admitted here, it was important for Dr. Neelam Andrade, the facility head, and her team to monitor patients closely, keep a check on their disease progression and ensure that they acted quickly. qXR helped Dr. Andrade’s team by providing instant automated reporting of the chest X-rays. It also captured all clinical information, enabling the center to make their process completely paperless.
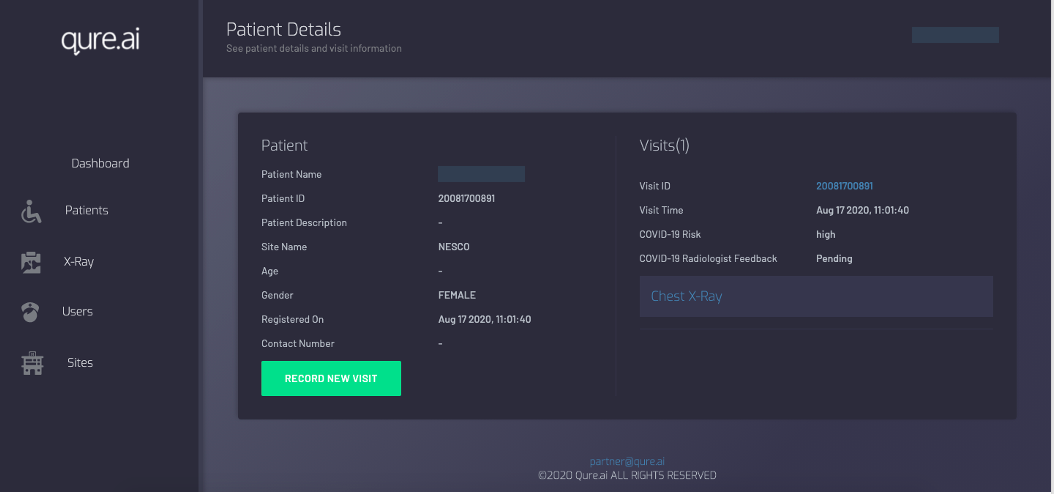
The patient summary screen of qXR web portal
“Since the patients admitted here are confirmed cases, we take frequent X-rays to monitor their condition. qXR gives instant results and this has been very helpful for us to make decisions quickly for the patient on their treatment and management.”
- Dr Neelam Andrade, Dean, NESCO COVID centre
SevenHills Hospital, Andheri
Located in the heart of the city’s suburbs, SevenHills Hospital was one of the first hospitals that were revived by MCGM as a part of COVID-19 response measures.
The center played a critical role on two accounts:
- Because patients were referred to the hospital for RT-PCR testing from door-to-door screening by MCGM. If found positive, they were admitted at the center itself for quarantine and treatment.
- With close to 1000 beds dedicated to COVID-19 patients alone, the doctors needed assistance for easy management of critical patients and to monitor their cases closely.
As with all COVID-19 cases, chest x-rays were taken of the admitted patients periodically to ascertain their lung condition and monitor the progress of the disease. All x-rays were then read by the head radiologist, Dr. Bhujang Pai, the next day, and released to the patient only post his review and approval. This meant that on most mornings, Dr. Pai was tasked with reading and reporting 200-250 x-rays, if not more. This is where qXR simplified his work.
Initially, we deployed the software on one of the two chest X-ray systems. However, after stellar feedback from Dr. Pai, our technology was installed in both the machines. In this manner AI, pre-read was available for all chest X-rays of COVID-19 patients from the center.
Where qXR adds most value:
- several crucial indications are reported up by qXR
- percentage lung affected helps to quantify improvement/deterioration in the patient lung and provide an objective assessment of the patient’s condition
- pre-filled PDF report downloadable from the Qure portal makes it easier to finalize the radiology report prior to releasing to the patient, especially in a high-volume setting

Dr. Pai reviews and finalizes the qXR report prior to signing it off
“At SevenHills hospital, we have a daily load of ~220 Chest X-rays from the admitted COVID-19 cases, sometimes going up to 300 films per day. Having qXR has helped me immensely in reading them in a much shorter amount of time and helps me utilise my time more efficiently. The findings from the software are useful to quickly pickup the indications and we have been able to work with the team, and make suitable modifications in the reporting pattern, to make the findings more accurate. qXR pre-fills the report which I review and edit, and this facilitates releasing the patient reports in a much faster and efficient manner. This obviously translates into better patient care and treatment outcomes. The percentage of lung involvement which qXR analyses enhances the Radiologist’s report and is an excellent tool in reporting Chest radiographs of patients diagnosed with COVID infection.”
– Dr Bhujang Pai, Radiology Head, SevenHills Hospital
Challenges and learnings
During the course of the pandemic, Qure has assisted MCGM with providing AI analyses for thousands of chest x-rays of COVID-19 suspects and patients. This has been possible with continued collaboration with key stakeholders within MCGM who have been happy to assist in the process and provide necessary approvals and documentation to initiate work. However, different challenges were posed by the sites owing to their varied nature and the limitations that came with them.
We had to navigate through various technical challenges like interrupted network connections and lack of an IT team, especially at the makeshift COVID centers. We crossed these hurdles repeatedly to ensure that the x-rays from these centers were processed seamlessly within the stipulated timeframe, and the x-ray systems being used were serviced and functioning uninterrupted. Close coordination with the on-ground team and cooperation from their end was crucial to keep the engagement smooth.
This pandemic has been a revelation in many ways. In addition to reiterating that a virus sees no class or creed, it also forced us to move beyond our comfort zones and take our blinders off. Owing to limitations posed by the pandemic and subsequent movement restrictions, every single deployment of qXR by Qure was done entirely remotely. This included end-to-end activities like coordination with the key stakeholders, planning and execution of the deployment of the software, training of on-ground staff, and physicians using the portal/mobile app in addition to continuous operations support.
Robust and smart technology truly made it possible to implement what we had conceived and hoped for. Proving yet again that if we are to move ahead, it has to be a healthy partnership between technology and humanity.
Qure is supported by ACT Grants and India Health Fund for joining MCGM’s efforts for the pandemic response using qXR for COVID-19 management.